Artificial intelligence explained in simple terms means understanding how machines learn, think, and act in ways that feel almost human. Today, Artificial Intelligence (AI) powers everyday tools, from search engines to smart assistants, shaping how you work, shop, and make decisions. Instead of following rigid instructions, modern AI relies on Machine Learning (ML) to analyze data, recognize patterns, and improve over time.
Behind the scenes, Intelligent systems use advanced models to deliver faster answers, smarter recommendations, and real-time insights. As AI adoption grows across healthcare, finance, and business, knowing how this technology works helps you separate hype from reality. This guide breaks down artificial intelligence in clear language, so you can understand its impact and future with confidence.
What Is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?

Artificial intelligence refers to computer systems designed to display Human-like intelligence. These systems learn, reason, and act using data rather than instinct. At its core, Artificial Intelligence (AI) powers Intelligent systems that mimic human thinking through Decision-making systems, advanced Pattern recognition, and adaptive learning models.
Today’s AI-powered applications operate as Smart machines. They analyze information, generate Data-driven insights, and perform tasks once reserved for people. From voice assistants to medical tools, Artificial Intelligence (AI) blends Cognitive computing with automation to deliver speed, scale, and accuracy across industries.
How Artificial Intelligence Works

Artificial intelligence works by combining Training data, algorithms, and computing power into learning models. Data flows into algorithms that identify patterns through Feature extraction and statistical learning. Over time, the system improves using Model tuning to deliver sharper predictions and smarter actions.
Learning methods define how Artificial Intelligence (AI) adapts. Supervised learning, Unsupervised learning, Semi-supervised learning, Self-supervised learning, and Reinforcement learning help systems evolve. These approaches reduce errors, prevent Model drift, and improve performance across the entire AI lifecycle.
Core AI Technologies Explained

Several core technologies drive modern Artificial Intelligence (AI). Machine Learning (ML) enables systems to learn from data without explicit instructions. Deep Learning builds on this using layered architectures that excel at complex tasks like vision and speech.
At the heart of these systems sit Neural Networks, including Artificial neural networks and Deep neural networks. Combined with Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Computer Vision, these technologies allow machines to understand language, images, and context with remarkable precision.
Generative AI and Large Language Models (LLMs)

Generative AI (Gen AI) creates original content using learned patterns. It supports Text generation, Image generation, and Video generation through advanced architectures. Popular techniques include Diffusion models, Variational autoencoders (VAEs), and Transformer models.
Most modern tools rely on Foundation Models and Large Language Models (LLMs). Platforms such as GPT models, ChatGPT, BERT, Bard, Copilot, and Midjourney use Prompt-based generation for scalable Content creation AI. These systems often improve via Fine-tuning, Reinforcement learning with human feedback (RLHF), and Retrieval augmented generation (RAG).
AI Agents and Agentic AI
AI Agents operate as Autonomous systems that plan and act without constant human input. Unlike basic chatbots, they complete workflows, use tools, and adapt to changing goals across environments.
Agentic AI coordinates multiple agents into a single system. These networks collaborate to solve complex tasks using shared context and decision logic. This shift marks a new phase for Artificial Intelligence (AI) where action follows intelligence, not just prediction.
Types of Artificial Intelligence

Most real-world systems today fall under Weak AI (Narrow AI). These systems focus on specific tasks such as translation, recommendations, or image recognition. They perform exceptionally well within defined limits.
In contrast, Strong AI (Artificial General Intelligence – AGI) remains theoretical. AGI would learn, reason, and adapt across domains like a human. While research continues, no existing system has reached this level of general intelligence.
Benefits of Artificial Intelligence

Artificial intelligence improves efficiency through AI automation. Organizations gain faster decisions, reduced errors, and scalable operations using Predictive analytics and real-time insights.
In healthcare, manufacturing, and finance, Artificial Intelligence (AI) enables safer processes and continuous availability. These benefits drive innovation while lowering costs, especially when paired with Cloud computing and Big data platforms.
Real-World AI Use Cases
Across industries, Artificial Intelligence (AI) supports AI chatbots, Virtual assistants, and AI in customer support. In finance, Fraud detection systems monitor transactions using anomaly detection models.
Healthcare uses AI in healthcare for diagnostics and imaging. Businesses rely on Personalized marketing, Resume screening AI, AI in recruitment, Predictive maintenance, AI in application development, AI in IoT, and AI-driven analytics to stay competitive.
| Industry | AI Application | Impact |
| Healthcare | Diagnostics | Faster, accurate decisions |
| Finance | Fraud detection | Reduced financial risk |
| Retail | Personalized marketing | Higher engagement |
| IT | Predictive maintenance | Lower downtime |
AI Challenges, Risks, and Limitations
Despite its power, Artificial Intelligence (AI) faces serious risks. Data privacy, Data poisoning, and Cybersecurity risks threaten system reliability. Attacks on Model integrity can compromise outcomes and trust.
Bias remains a concern due to Algorithmic bias in data and models. Addressing these issues requires Bias mitigation, strong AI risk management, and continuous monitoring to ensure fairness and safety.
AI Ethics, Governance, and the Future of AI
AI Ethics focuses on building systems that are transparent, fair, and accountable. Ethical AI development promotes AI transparency, Accountability in AI, and Fairness and inclusion.
Strong AI Governance frameworks support Responsible AI, Explainable AI, and Secure AI systems. Compliance with Regulatory compliance, including GDPR and AI, ensures trust as Multimodal models and advanced automation reshape the future.
History and Evolution of AI
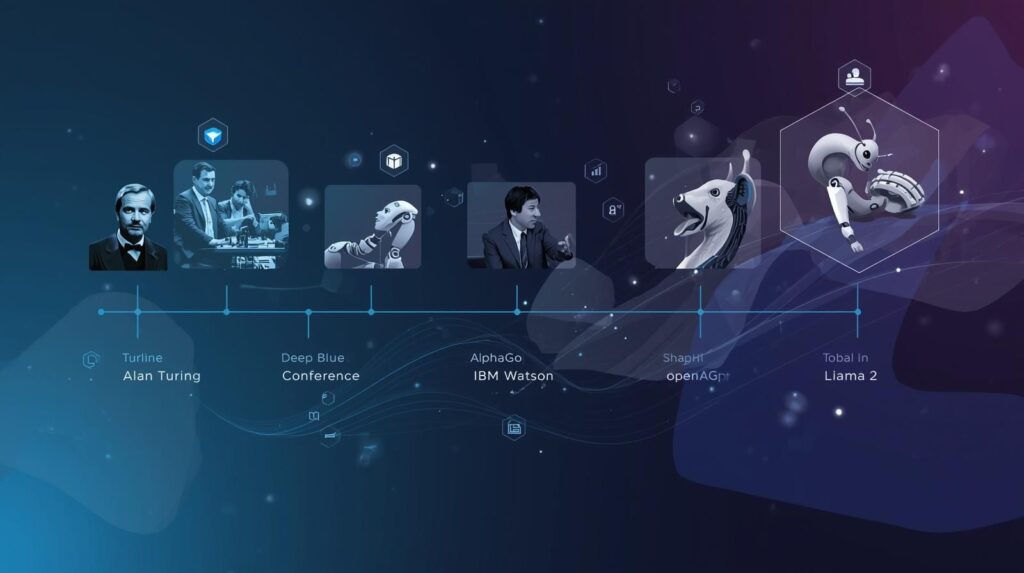
The roots of Artificial Intelligence (AI) trace back to Alan Turing and the Turing Test. The term itself emerged at the Dartmouth AI Conference, led by John McCarthy.
Milestones include Deep Blue vs Kasparov, IBM Watson, and AlphaGo by DeepMind. Today, innovation continues through OpenAI, Llama 2, and large-scale systems powered by Cloud computing and Big data, marking a new AI era in 2026.
“Artificial intelligence is not replacing humans; it is redefining what humans can achieve.”
This complete guide shows how Artificial Intelligence (AI) continues to transform industries, economies, and everyday life across the United States, setting the foundation for a smarter and more connected future.
FAQs
What are the 4 types of artificial intelligence?
The four types of artificial intelligence are based on capability. Reactive AI responds only to current input. Limited memory AI learns from past data, which most modern AI uses today. Theory of mind AI is still experimental. Self-aware AI remains theoretical and does not exist yet.
What jobs will AI replace?
AI will mainly replace repetitive and rule-based jobs. These include data entry, basic customer support, simple bookkeeping, and routine manufacturing roles. However, AI also creates new jobs in AI development, data analysis, cybersecurity, and human-AI collaboration rather than replacing all work.
What is artificial intelligence in simple words?
Artificial intelligence is when computers are taught to think and learn like humans. AI systems use data to make decisions, recognize patterns, and solve problems. Examples include voice assistants, recommendation systems, and self-driving features in cars.
What are the top 3 AI stocks to buy now?
Popular AI-focused stocks often mentioned by analysts include NVIDIA for AI chips, Microsoft for AI-powered cloud and software, and Alphabet (Google) for AI research and products. Stock performance changes often, so personal research or financial advice is recommended.
What AI stock is Warren Buffett buying?
Warren Buffett has historically invested in companies using AI rather than pure AI startups. Apple remains one of his largest holdings, benefiting from AI integration across devices and services. He focuses on long-term value, not short-term AI hype.
Who are the big 4 of AI?
The “Big 4” of AI typically refers to Google, Microsoft, Amazon, and Meta. These companies lead in AI research, cloud infrastructure, large language models, and real-world AI applications used by millions globally.
